Patient Prognosis - Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Surival Rate
Lung cancer is one of the most common and serious cancers worldwide, but understanding survival rates can help provide clarity and hope. This webpage breaks down survival statistics in a simple, approachable way to help you better understand the factors that impact outcomes and the importance of early detection and treatment.
Data from Sources
Keytruda

Combination Therapy in Squamous mNSCLC
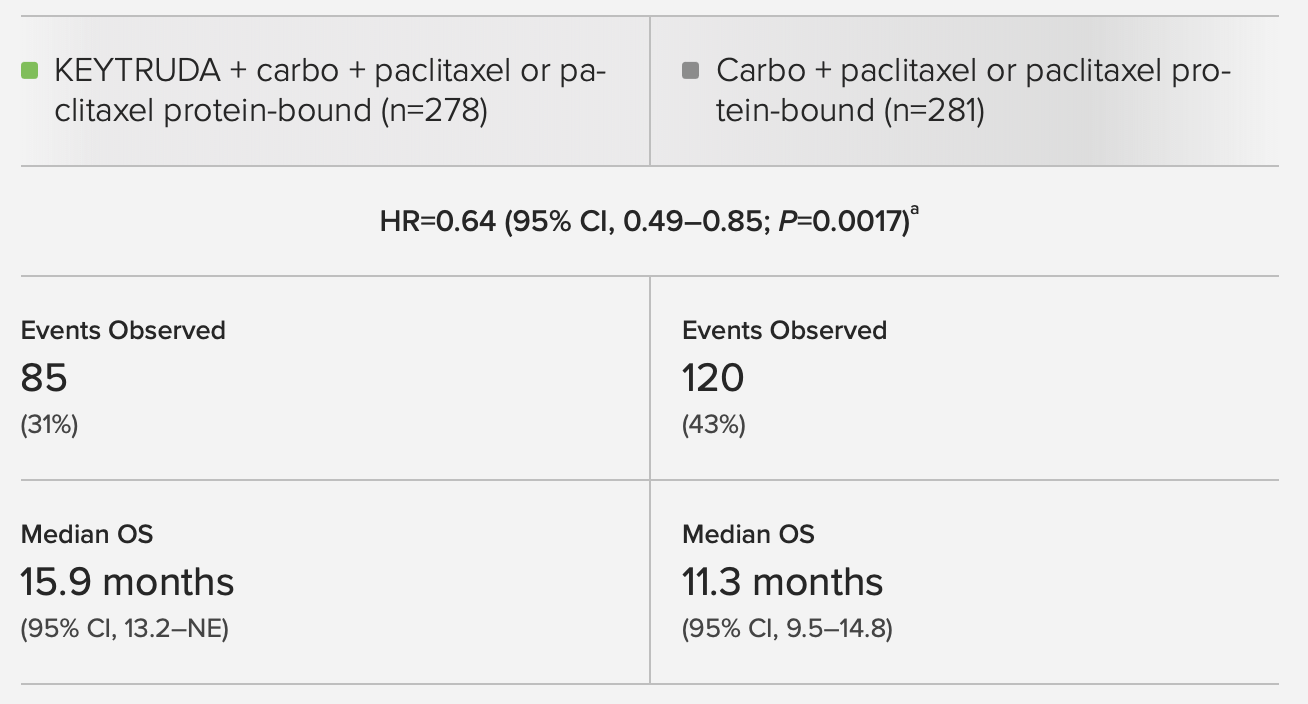
Fig 1.1 Overall Survival
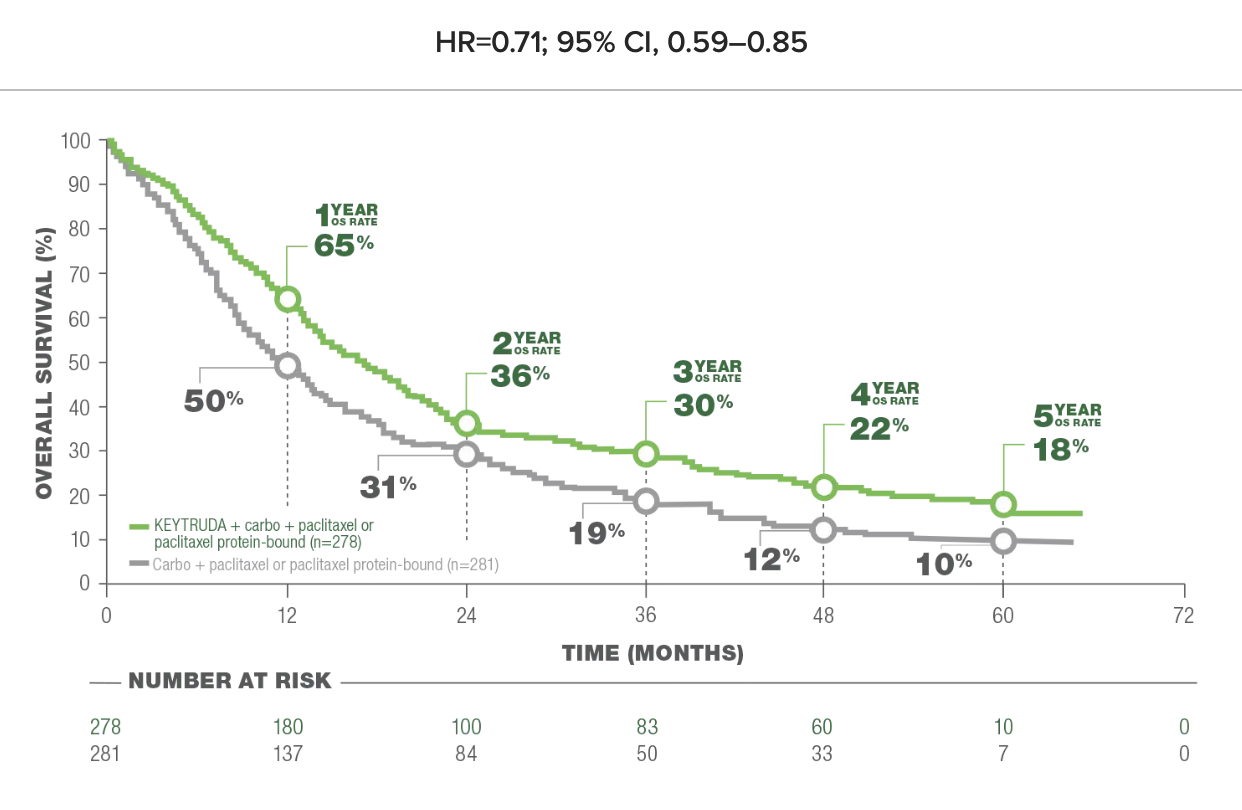
Fig 1.2 Overall Survival (OS) in Patients With or Without PD-L1 Expression
LIMITATION: This post-hoc analysis (median follow-up: 56.9 months) in KEYNOTE-407 was exploratory in nature and occurred after the protocol-specified final analysis. No formal statistical testing was planned for this updated analysis and, therefore, no statistical conclusions can be drawn. Trial participants in either study arm could receive subsequent anti-cancer therapy. CROSSOVER RATE: 50.9%; 117 patients in the carbo + paclitaxel or paclitaxel protein-bound group crossed over to KEYTRUDA as monotherapy on-study and an additional 26 received subsequent anti-PD-L1 therapy outside the study.
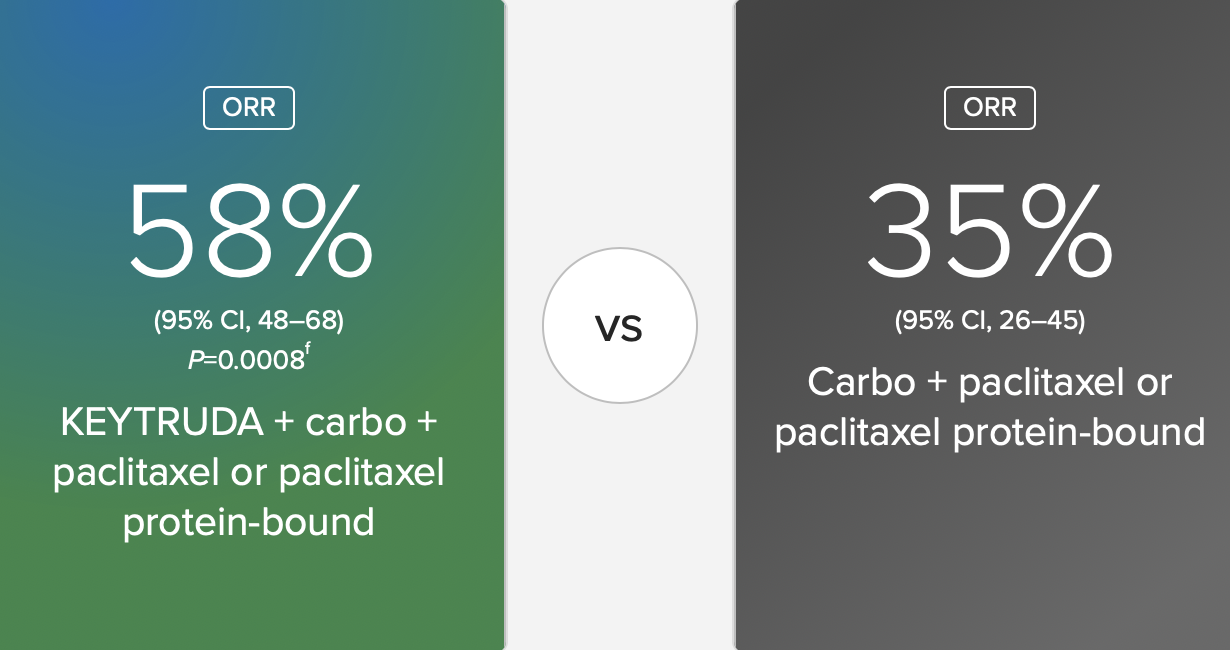
Fig 1.3 Objective Response Rate (ORR): Over Half of Patients Responded With KEYTRUDA + carbo + paclitaxel or paclitaxel protein-bound
Clinical Efficacy of Keytruda in NSCLC: The Keynote-407 study demonstrates that Keytruda in combination with chemotherapy significantly improves overall survival and progression-free survival for patients with squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Patients receiving the Keytruda-combination therapy had higher survival rates compared to chemotherapy alone.
Response Rate Improvements: The combination therapy also showed improved objective response rates, indicating a higher percentage of patients achieved measurable tumor shrinkage.
Duration of Response: Treatment with Keytruda extended the duration of response compared to chemotherapy alone, meaning patients experienced prolonged tumor control.
PD-L1 Expression Subgroup Analysis: The efficacy of Keytruda was observed across all levels of PD-L1 expression, making it a versatile option for patients with varying biomarker profiles.
Tolerability and Safety: The safety profile of the combination therapy was consistent with known adverse effects, with immune-mediated side effects manageable in most cases.
Purpose of Resource: This resource highlights the survival rates and efficacy of Keytruda in combination therapy for lung cancer patients.
Goal: Compare survival rates of patients undergoing Keytruda therapy with or without PD-L1 expression.
Using this Resource:
Identifying Subgroup Comparisons
- Use Fig 1.1 to understand the general overall survival trends for lung cancer patients treated with Keytruda.
- Use Fig 1.2 to explore subgroup-specific data (e.g., PD-L1 positive vs. negative).
Extract Actionable Items
- Identify how PD-L1 expression influences survival outcomes and use this insight when discussing treatment with healthcare providers.
National Library of Medicine

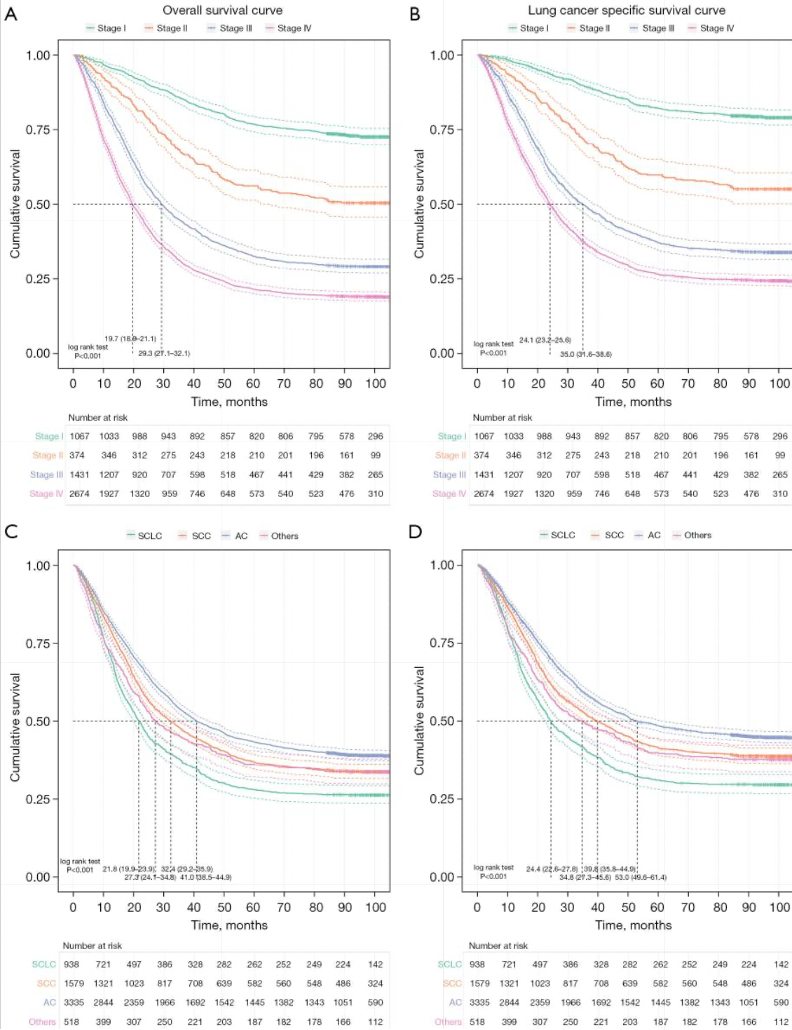
Fig 2.1 Survival curves of lung cancer patients with specific diagnosis of pathological stage/histological classification.
The article likely explains how Keytruda, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, works by targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, enabling the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells effectively.
Additional studies or real-world applications of pembrolizumab in hospitals in China confirm its efficacy beyond clinical trial settings, highlighting its robustness in diverse patient populations.
Similar to the article above, this research paper concludes that combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy may synergistically enhance outcomes by reducing tumor burden (via chemotherapy) and stimulating immune responses (via immunotherapy). Rather than focusing on immediate changes, the long-term follow-up data likely provide insights into survival benefits, quality of life, and potential resistance mechanisms.
Purpose of Resource: This multicenter study analyzes the survival of over 7,300 lung cancer patients by pathological stage and histological classification.
Goal:Examine how early diagnosis and specific cancer types influence survival rates.
Using this Resource:
Stage Based Survival
- Access the table or graph showing survival by pathological stage to identify the impact of early-stage diagnosis.
Historical Insights
- Compare outcomes for small-cell vs. non-small-cell lung cancer patients for tailored treatment discussions.
Nature Briefing

Prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
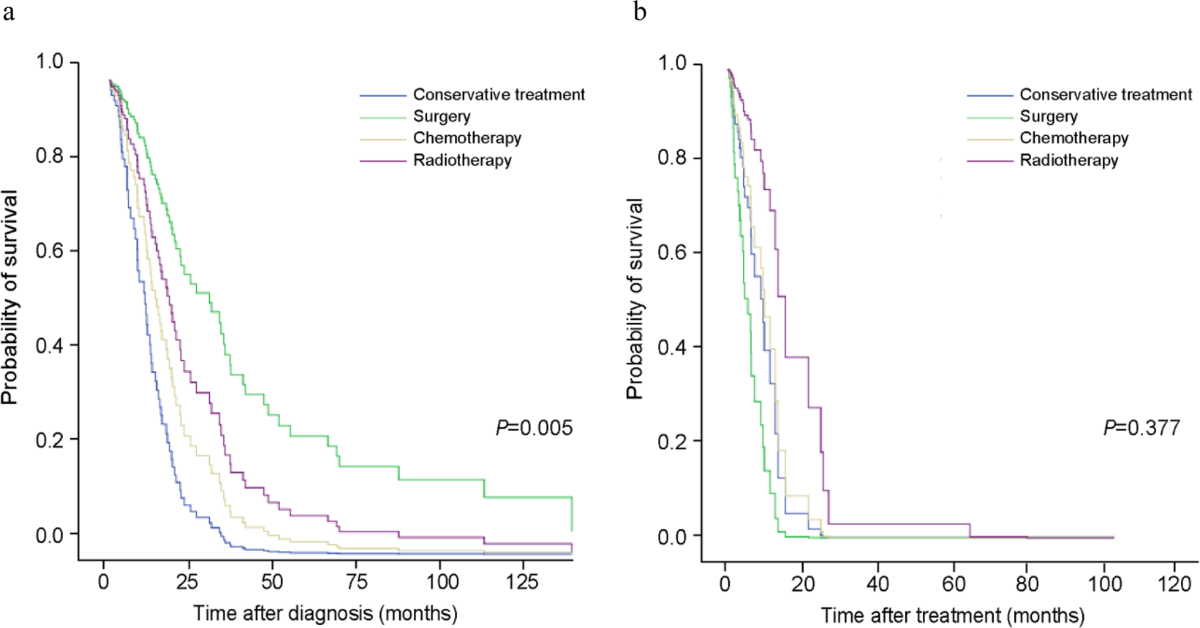
Comparison of survival probability according to treatment modality in GAP stage
Purpose of Resource: Provides insights into the prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Goal: Investigate how comorbidities affect lung cancer outcomes.
Using this Resource:
Explore Impact of Comorbidities
- Use the survival curves to understand how additional health conditions (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis) impact lung cancer prognosis.
Broaden Context
- Combine this resource with Keytruda data to evaluate if similar comorbidities were considered in treatment studies.
Consumer Insights and Goals
The goal of this website is to provide lung cancer patients, caregivers, or medical professionals with a comprehensive understanding of survival rates, treatment efficacy, and prognostic factors. These insights help them:
- Compare Treatment Outcomes: Evaluate how different treatments (e.g., Keytruda) affect survival rates for lung cancer patients, particularly in subgroups with specific conditions (e.g., PD-L1 expression).
- Understand Prognostic Factors:Identify how factors like histological classification or pathological stage influence survival rates.
- Make Informed Decisions:Use comparative insights to discuss treatment options with healthcare providers, maximizing outcomes.
- Support Early Detection Goals:Explore data and trends emphasizing the importance of early intervention in improving survival rates.
Other Potential Action Items
Clinical practice enhancements:
- o Expand PD-L1 Testing: Ensure widespread availability and utilization of PD-L1 testing for NSCLC patients to guide treatment decisions effectively.
- o Develop Multidisciplinary Teams: Integrate oncologists, pathologists, and pharmacologists to optimize personalized treatment plans, particularly for squamous NSCLC patients.
- o Educate Healthcare Providers: Conduct training sessions and workshops to update healthcare providers on Keytruda's efficacy, safety, and administration protocols.
R&D
- o Monitor Long-Term Outcomes: Conduct extended follow-ups and real-world studies to assess the long-term benefits and resistance mechanisms associated with Keytruda.
- o Explore Additional Combinations: Investigate other chemotherapy or targeted therapy combinations to expand the therapeutic potential of Keytruda.
- o Advance Biomarker Research: Identify and validate additional biomarkers to refine patient selection further and enhance precision medicine.
Patient centric initiatives:
- o Promote Awareness of Combination Therapies: Educate patients about the benefits of combination therapies, including improved survival rates and durable responses.
- o Improve Side-Effect Management: Develop patient-focused resources for managing immune-related adverse effects, ensuring adherence to therapy and improved quality of life.
Sample Analysis
How does one actually apply the information above to themselves?
Sample Consumer Goal
A patient with stage II non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and PD-L1 expression wants to understand how treatment options (e.g., Keytruda) improve their survival compared to general outcomes for NSCLC patients.
Using the Keytruda Data
Use Fig 1.2 (Overall Survival for PD-L1 Positive/Negative Patients).
- Highlight the data point for PD-L1 positive patients showing improved survival rates.
- Compare it to the general survival trend for NSCLC patients in the same stage.
Consult National Library of Medicine
- Highlight the average survival percentage for stage II NSCLC patients.
- Compare these general statistics to the Keytruda data for PD-L1 positive patients.
Explore Nature Briefing
- Highlight how the comorbidity affects survival compared to patients without it.
- Integrate this insight with previous data to understand the consumer's unique situation.
Final Analysis
The patient can see that Keytruda significantly improves survival outcomes for PD-L1 positive patients (Keytruda Data, Fig 1.2). They can contextualize their stage-specific prognosis using general survival trends (National Library of Medicine). They can evaluate the potential impact of additional comorbidities on their prognosis (Nature Briefing).